Unleash the hidden power of psychological pricing! Go beyond basic pricing models and delve into the minds of your customers. This guide equips you with the most effective pricing strategies to skyrocket sales and attract new customers.
We’ll guide you in leveraging consumer psychology to maximize demand and outpace your competitors. Unlock your business’s true potential and dominate the market. Keep reading!
What is Psychological Pricing?
Psychological pricing is not just about numbers. It’s a strategic tool in the arsenal of every business. It’s about understanding human behavior and leveraging that knowledge to influence purchasing decisions. Instead of relying solely on cost-based pricing models, psychological pricing takes a deeper dive into consumer psychology.
By tapping into the intricate workings of the human mind, psychological pricing aims to shape perceptions of value and drive sales. It recognizes that consumers are not always rational actors but are influenced by a myriad of psychological factors when making purchasing decisions.
Psychological pricing relies on common cognitive biases. It includes the anchoring effect and the left-digit bias. By presenting a higher-priced option first, you establish a reference point (or anchor) that makes subsequent options seem more reasonable and enticing. Additionally, ending prices with .99 or .95 creates the illusion of a bargain, tapping into consumers’ tendency to focus on the leftmost digits of a price.
Pricing psychology is about what drives consumer behavior and using that knowledge to your advantage. It’s about creating a pricing strategy that works—resonates with your target audience and compels them to make a purchase.
It’s not just about setting prices. It’s about understanding the psychology behind those prices and leveraging it to maximize profitability. So, the next time you’re setting prices for your products or services, remember the power of psychological pricing and put the best foot forward. Let’s look at different psychological pricing strategies.
Psychological Pricing Strategies
1. Price Anchoring
 Price anchoring leverages the human tendency to focus on the first piece of information given. By setting a high initial price, the “anchor,” you establish a reference that makes later prices seem more reasonable. This effect persuades customers to view subsequent offers as bargains, despite a high starting point. This tactic is crucial to launch new products or premium items.
Price anchoring leverages the human tendency to focus on the first piece of information given. By setting a high initial price, the “anchor,” you establish a reference that makes later prices seem more reasonable. This effect persuades customers to view subsequent offers as bargains, despite a high starting point. This tactic is crucial to launch new products or premium items.
For example—a software company introduces three pricing plans: a premium plan at $99 per month, a standard at $49, and a basic at $19. With the $99 anchor, the other plans appear more accessible, boosting their appeal.
💡Fact
Do you know 91% of Americans check for discounts before making a purchase?
2. Charm Pricing
 Charm pricing uses the simple trick of ending prices with the digit 9. This strategy taps into how consumers see prices ending in 9 as much lower than their rounded counterparts. For instance, most people view $19.99 as closer to $19 than $20. By using charm pricing, businesses create the illusion of a bargain, increasing the appeal of their products or services.
Charm pricing uses the simple trick of ending prices with the digit 9. This strategy taps into how consumers see prices ending in 9 as much lower than their rounded counterparts. For instance, most people view $19.99 as closer to $19 than $20. By using charm pricing, businesses create the illusion of a bargain, increasing the appeal of their products or services.
This approach is common in retail and hospitality. Especially among price-sensitive shoppers who look for perceived savings. Charm pricing is often used in sales promotions, clearance events, or everyday pricing. It encourages customers to purchase on the allure of a good deal. Its widespread recognition also makes it a low-risk, go-to strategy for businesses around the world.
For example—imagine a clothing store that’s introducing a new line of jeans. The store sets the price of these jeans at $39.99 instead of $40. Even though the price difference is only one cent, the price tag ending in “.99” makes the jeans appear significantly cheaper to most consumers. This perception comes from the initial ‘3’ in $39.99, which consumers subconsciously process as being closer to $30 than to $40, making them more likely to consider it a bargain and thus more likely to buy.
💡Fact
Did you know the charm pricing strategy—which involves ending prices in 9 or 99—boosts sales by 24%?
3. Decoy Pricing
 Decoy pricing is a clever tactic that involves adding a less attractive option—the decoy—to make other choices look better. The decoy’s price guides customers towards a target option that appears to offer the best value. This strategy uses consumers’ habit of comparing options against each other, not on their own merits.
Decoy pricing is a clever tactic that involves adding a less attractive option—the decoy—to make other choices look better. The decoy’s price guides customers towards a target option that appears to offer the best value. This strategy uses consumers’ habit of comparing options against each other, not on their own merits.
By using a decoy, businesses give the illusion of choice while nudging consumers towards a preferred product. This psychological pricing method is popular in industries like hospitality, electronics, and subscription services. It aims to boost sales by influencing decision-making. When used effectively, decoy pricing drives both customer decisions and business revenue.
For example—a movie theatre offers three popcorn sizes: small for $3, medium for $6.50, and large for $7. The medium-sized popcorn acts as a decoy. It is not much cheaper than the large one, but much more expensive than the small one. This pricing strategy makes the large popcorn appear to be a great deal in comparison—it’s only 50 cents more than the medium but offers significantly more popcorn. Consequently, most customers are likely to choose the large, seeing it as the best value for their money. This is a classic example of psychological pricing—decoy pricing, where the medium option is strategically priced to push customers towards the large popcorn.
4. Bundle pricing
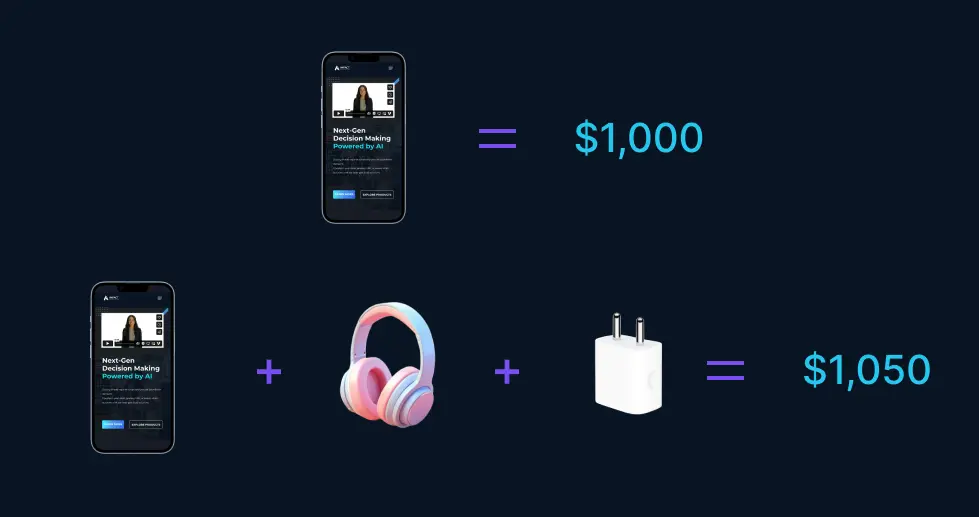 Bundle pricing is a pricing strategy where businesses offer multiple products or services together at a discount. This approach boosts value perception, enticing customers with savings and the convenience of one purchase. Businesses bundle related items to increase transaction value. This psychological pricing strategy works well in sectors like telecommunications, software, and entertainment.
Bundle pricing is a pricing strategy where businesses offer multiple products or services together at a discount. This approach boosts value perception, enticing customers with savings and the convenience of one purchase. Businesses bundle related items to increase transaction value. This psychological pricing strategy works well in sectors like telecommunications, software, and entertainment.
For example—a telecommunications company might bundle internet, cable TV, and phone services at a lower rate than buying each separately. This attracts price-sensitive customers, builds loyalty, and sets the company apart from competitors who sell services individually.
5. Flat-Rate Bids
Flat-rate bids, or fixed-price bidding, mean quoting one price for a service, no matter the work involved. This strategy offers simplicity and transparency, removing the uncertainty that comes with hourly or variable pricing. Customers appreciate knowing the cost upfront, which enables them to make decisions without fear of unexpected fees. Service-based businesses like freelancers, contractors, and consultants often use this approach. It simplifies the quoting process and builds trust.
For example—a graphic designer might charge a flat $1,000 to create a company logo, no matter how many revisions are needed. Flat-rate bids lead to quicker project approvals, higher client satisfaction, and fewer disputes about charges.
6. Price Appearance
Appearance pricing refers to how businesses present prices to customers. It aims to show value and justify the asking price. This strategy highlights a product or service’s features, benefits, and unique selling points. It emphasizes its value proposition instead of just focusing on the price. Price appearance works well for premium or luxury products and services. These are where quality, exclusivity, and brand perception are crucial.
For example—a high-end automobile manufacturer might highlight the advanced technology, superior craftsmanship, and prestigious brand heritage of its vehicles. This is to justify their premium prices. By enhancing the perceived value of their offerings, businesses charge higher prices. They also stand out from competitors and attract affluent or discerning customers who value quality.
Psychological Pricing Techniques
In addition to overarching marketing strategies, businesses also employ specific techniques to implement psychological pricing effectively. These techniques delve into the nuances of consumer psychology, exploiting cognitive biases and heuristics to shape purchasing decisions. Here are some key techniques.
1. Price Framing
Price framing involves presenting prices in a way that influences how they are perceived. This technique of psychological pricing includes emphasizing the value proposition of a product, highlighting savings compared to competitor prices, or framing prices in terms of small, digestible increments (e.g., daily or weekly rates). By framing prices in a favorable light, businesses enhance perceived value and encourage consumers to make purchases.
2. Scarcity and Urgency
Creating a sense of scarcity or urgency drives consumer behavior by tapping into the fear of missing out (FOMO). Limited-time offers countdown timers, and low-stock alerts are all techniques used to instil a sense of urgency and prompt immediate action. By leveraging the psychological principle of loss aversion, businesses compel consumers to act quickly to secure a perceived valuable opportunity.
3. Social Proof
Social proof involves leveraging the power of social influence to sway consumer behavior. Testimonials, reviews, ratings, and endorsements from satisfied customers serve as powerful forms of social proof, reassuring potential buyers and validating their decision to purchase. By highlighting the experiences of others, businesses instill confidence and credibility, mitigating perceived risks associated with making a purchase.
4. Personalization
Personalization involves tailoring pricing and promotional offers to individual consumer preferences and behaviors. By leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, businesses segment their customer base and deliver targeted pricing incentives, discounts, or promotions tailored to each customer’s unique needs and preferences. Personalized pricing not only enhances the customer experience but also increases the likelihood of conversion by delivering relevant and timely offers.
5. A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, involves experimenting with different types of psychological pricing strategies and measuring their psychological impact on consumer behavior. By systematically varying elements such as price points, product positioning, and promotional offers, businesses identify the most effective pricing tactics and refine their strategies accordingly. A/B testing provides valuable insights into consumer preferences and allows businesses to optimize their pricing strategies for maximum impact and profitability.
Conclusion
Psychological pricing offers a powerful yet nuanced approach to influencing customer behavior and driving sales growth. This comprehensive guide equips you with a valuable toolkit of strategies, from price anchoring and bundling to decoy pricing and effective price presentation. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your pricing strategy and unlock its full potential to propel your business forward.
Take the Next Step
Take action today and transform your pricing into a persuasive force that drives profitability and success.
Maximize profits and engage your customers with dynamic price optimization strategies. Leverage artificial intelligence- and machine learning-powered price optimization solutions to rise above your competition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective psychological pricing tactics for boosting sales?
This guide explores powerful strategies like anchoring (setting a reference price), charm pricing (ending prices in “.99”), and bundling (offering products together at a discount). Master these tactics and watch your sales soar!
How can I use psychological pricing without seeming manipulative?
Transparency is key! Focus on highlighting the value your product offers and frame your pricing around the benefits customers receive. Psychological pricing ethically nudges, not forces, purchase decisions.
Is psychological pricing suitable for all businesses and products?
Absolutely! While the ideal strategies may differ, psychological pricing offers valuable tools for any business. This guide explores effective tactics across various industries, from retail to service-based businesses.





